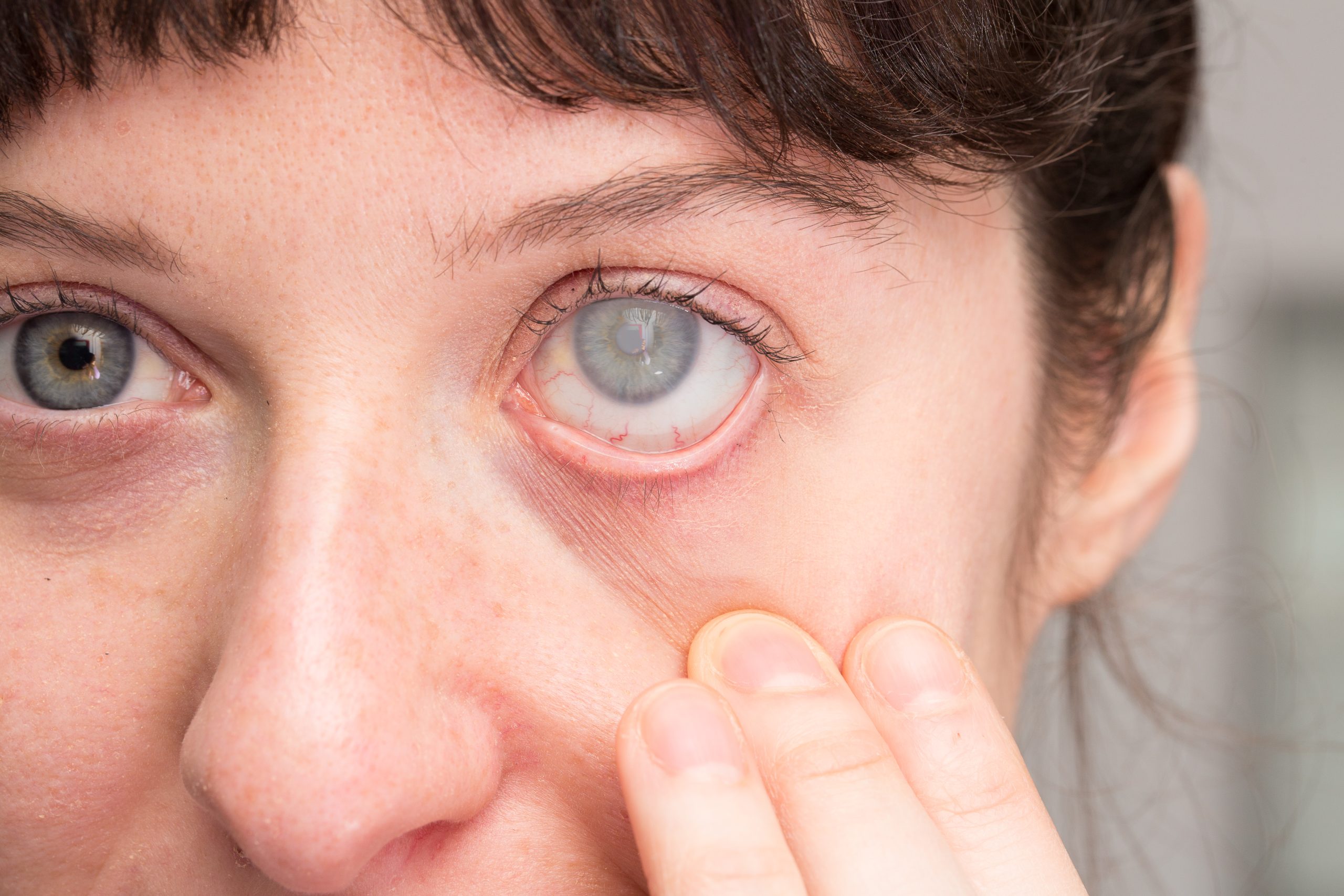
Are you tired of red, teary eyes? Are you frustrated by persistent eye pain or that mysterious white spot on your cornea? Well, look no further! In this article, we’ll dive into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for corneal ulcers. These pesky little sores on your eye’s clear tissue can be caused by infections like bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. If you wear contact lenses, especially if you sleep in them, you’re at a higher risk. Previous eye surgeries and certain eye diseases can also increase your chances. But fear not! With prompt treatment, including eye drops and pain management, you can effectively manage and treat corneal ulcers, preserving your precious vision.
Overview and Definition
To understand corneal ulcers, it is important to start with an overview and definition of this condition. A corneal ulcer is an open sore on the cornea, the clear tissue layer that covers the front of the eye. It is often caused by infection, with bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites being the common culprits. Bacterial infections, such as staphylococcus or pseudomonas, are frequent causes, while viral infections like herpes simplex or varicella can also lead to corneal ulcers. Fungal infections, such as Fusarium or Candida, are rare but possible. People who wear contact lenses, especially extended-wear soft contacts, are at higher risk due to the potential for trapped bacteria or particles under the lens. Other risk factors include corneal dystrophies, inherited eye conditions that can increase the likelihood of corneal ulcers.
Diagnosis of corneal ulcers involves using a dye and slit lamp microscope to examine the cornea, and a sample may be taken for lab analysis. Treatment often involves prescribing antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops, depending on the cause of the ulcer. Severe cases may require corneal transplant surgery. Regular follow-up with the doctor is necessary to monitor progress and ensure proper healing. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for corneal ulcers is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention, which can help prevent complications and minimize the risk of vision loss.
Risk Factors
Wearing contact lenses, especially extended-wear soft contacts, puts you at a higher risk for corneal ulcers. This is because the reduced oxygen supply and the potential for bacterial contamination can increase the likelihood of infection. It is important to be aware of the risk factors associated with corneal ulcers in order to prevent infection and protect your vision. Here are three key risk factors to consider:
- Contact lens hygiene: Poor contact lens hygiene, such as not properly cleaning and disinfecting your lenses, can increase the risk of corneal ulcers. It is crucial to follow proper hygiene practices to minimize the chance of infection.
- Diabetes and corneal ulcers: Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to developing corneal ulcers due to their compromised immune system and reduced ability to fight off infections. It is essential for those with diabetes to monitor their eye health closely and seek prompt medical attention if any symptoms arise.
- Shingles and corneal ulcers: Shingles, a viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, can affect the cornea in some cases. This can lead to corneal ulcers and potential vision loss. If you have had shingles, it is important to be vigilant about your eye health and seek medical advice if any concerns arise.
Understanding these risk factors and taking appropriate measures to prevent infection can help safeguard your vision and reduce the likelihood of corneal ulcers.
Prevalence and Importance
Corneal ulcers are a significant healthcare concern and require prompt medical attention. The prevalence of corneal ulcers highlights the importance of proper eye care and hygiene. Between 30,000 and 75,000 corneal ulcers occur each year in the U.S., and approximately 12% of all corneal transplants are performed due to corneal ulcers. The high prevalence of corneal ulcers underscores the need for prevention strategies and early detection.
Complications and risks associated with corneal ulcers can be severe. If left untreated, corneal ulcers can cause permanent damage and even blindness. Vision loss can occur as a result of corneal ulcers, and scarring on the cornea is also a possible complication. Therefore, it is crucial to seek prompt medical treatment to prevent these long-term effects.
Prevention strategies play a vital role in reducing the prevalence and importance of corneal ulcers. Proper hygiene, such as washing hands before touching the eyes and cleaning and disinfecting contact lenses, can help prevent bacterial contamination. Removing contact lenses before sleeping and avoiding swimming or showering while wearing them can also reduce the risk of corneal ulcers.
In terms of treatment options, prompt and appropriate treatment is necessary to prevent complications. Treatment depends on the cause of the corneal ulcer and may involve the use of antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops. In severe cases, a corneal transplant may be required. Regular follow-up with an eye care provider is essential for monitoring the progress and ensuring proper healing.
Symptoms
When it comes to symptoms of a corneal ulcer, you may experience a red, teary, bloodshot eye. Eye pain or ache is also common, along with the presence of pus or other discharge. Blurred vision may occur as well. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications and vision loss.
Red, teary, bloodshot eye
One of the symptoms of a corneal ulcer is the presence of redness, tearing, and a bloodshot appearance in your eye. This can be a distressing experience, causing discomfort and affecting your daily activities. Here are three emotional responses you may have when experiencing these symptoms:
- Frustration: The redness, teary eye, and bloodshot appearance can make you feel frustrated as they can interfere with your vision and overall well-being.
- Anxiety: The presence of these symptoms may cause anxiety as you worry about the underlying cause of the corneal ulcer and potential complications that could arise.
- Disruption: These symptoms can disrupt your daily life, making it difficult to perform tasks that require clear vision and causing discomfort and pain.
If you are experiencing redness, tearing, or a bloodshot eye, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Eye pain, eye ache
If you experience eye pain or aching, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Eye pain can be a symptom of various underlying conditions, including corneal ulcers. Common causes of eye pain include infections, such as bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections, as well as corneal injuries or exposure to chemicals or small particles. To manage eye pain, treatment options may include prescribing antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops, oral painkillers, or dilating drops. Preventive measures to reduce the risk of eye pain include proper hygiene, such as washing hands before touching the eyes, avoiding wearing contact lenses overnight, and seeking prompt treatment for eye infections. Coping with eye ache involves following the prescribed treatment plan and regular follow-up with your healthcare provider.
Pus or other eye discharge
If you’re experiencing eye pain or aching, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment for conditions such as corneal ulcers. One of the symptoms that you may experience is pus or other eye discharge. This can be a sign of an infection in the cornea and should not be ignored. Here are some important points to keep in mind regarding this symptom:
- Eye discharge: Pus or other types of discharge from the eye can indicate the presence of an infection in the cornea. It may be yellow or green in color and can be accompanied by redness and swelling.
- Treatment options: The treatment for corneal ulcers with pus or discharge typically involves the use of antibiotic eye drops or ointments to eliminate the infection. In severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Complications: If left untreated, corneal ulcers can lead to serious complications, such as vision loss or even permanent damage to the cornea. Prompt medical intervention is crucial to prevent these complications.
To prevent corneal ulcers and eye discharge, it is important to practice good hygiene, especially if you wear contact lenses. Make sure to follow proper hygiene practices, such as washing your hands before touching your eyes, cleaning and disinfecting your contact lenses regularly, and avoiding wearing them overnight. By taking these precautions, you can reduce the risk of developing corneal ulcers and experiencing eye discharge.
Blurred vision
If you experience blurred vision, it could be a symptom of a corneal ulcer, and seeking immediate medical attention is crucial. Blurred vision is a common symptom of corneal ulcers and can occur due to the damage and inflammation of the cornea. There are several causes and risk factors for corneal ulcers, including bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections. People who wear contact lenses, especially extended-wear soft contacts, are at higher risk due to the potential for bacterial or particle contamination. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and vision loss. Treatment options may include antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops, oral painkillers, and corneal transplant surgery in severe cases. To prevent corneal ulcers, it is important to practice good hygiene, properly clean and disinfect contact lenses, and seek immediate medical attention for eye infections or vision changes.
Causes and Prevention
To prevent corneal ulcers, practice proper eye care and hygiene. Here are some important tips to keep in mind:
- Contact lens hygiene: If you wear contact lenses, it is crucial to follow proper hygiene practices. This includes cleaning and disinfecting your lenses regularly, as well as replacing them according to the recommended schedule. Avoid sleeping in your lenses, as this increases the risk of corneal ulcers.
- Corneal ulcer risk factors: Be aware of the risk factors that can increase your chances of developing corneal ulcers. These include wearing contact lenses, especially overnight, having dry eyes, incomplete eyelid closure, a history of shingles or cold sores, and certain eye diseases or surgeries. Take extra precautions if you have any of these risk factors.
- Infection prevention: To reduce the risk of corneal ulcers, take steps to prevent eye infections. Wash your hands thoroughly before touching your eyes or handling contact lenses. Avoid sharing towels or eye makeup with others. And if you do develop an eye infection, seek prompt treatment to prevent it from progressing to a corneal ulcer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
When diagnosing and treating a corneal ulcer, your eye care provider will typically start by performing a thorough examination of your eye. Diagnostic methods commonly used include using a dye and slit lamp microscope to examine the cornea. This allows the provider to assess the severity and location of the ulcer. In some cases, a sample from the ulcer may be taken for lab analysis to determine the exact cause of the ulcer.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment options will be discussed. Medication options for corneal ulcers often involve prescribing antibiotic, antiviral, or antifungal eye drops, depending on the cause of the ulcer. These medications are aimed at fighting the underlying infection and promoting healing. In some cases, oral painkillers or dilating drops may be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Severe cases of corneal ulcers may require surgical interventions. This can include corneal transplant surgery, where a damaged or infected cornea is replaced with a healthy donor cornea. Your eye care provider will discuss the risks and benefits of surgery and determine if it is necessary in your specific case.
After treatment, follow-up care is crucial to monitor the healing process and ensure that the ulcer is resolving. Your eye care provider will schedule regular check-ups to assess your progress and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In addition to traditional medical treatments, alternative treatments such as the use of certain herbs, vitamins, or homeopathic remedies may be suggested. However, it is important to discuss these options with your eye care provider before trying them, as their effectiveness is not well established and they may interact with prescribed medications.
Outlook and Living With
As you continue your journey of living with a corneal ulcer, it is important to understand the outlook and potential challenges that may arise. Here are some key points to consider:
- Long-term effects: Living with corneal ulcers can have lasting effects on your vision. Depending on the severity of the ulcer and the effectiveness of treatment, you may experience minor changes or more significant vision loss. It is crucial to work closely with your eye care provider to monitor your condition and address any changes in your vision.
- Coping strategies: Dealing with a corneal ulcer can be emotionally challenging. It is important to find healthy ways to cope with the stress and frustration that may come with the condition. This can include practicing relaxation techniques, seeking support from loved ones, or engaging in activities that bring you joy and distraction.
- Support groups and vision rehabilitation: Connecting with others who have experienced or are currently living with corneal ulcers can provide invaluable support and understanding. Support groups or online communities can offer a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and learn coping strategies. Additionally, vision rehabilitation services can help you adapt to any vision changes and maximize your visual function.
Additional Information
Gain a deeper understanding of corneal ulcers by exploring relevant additional information. Corneal ulcers can lead to various complications, including vision loss, cornea scarring, and other long-term damage. It is important to be aware of the risk factors and take proper precautions, especially for those who wear contact lenses. Practicing good hygiene practices, such as washing hands before touching the eyes and properly cleaning and disinfecting contact lenses, can help reduce the risk of corneal ulcers.
To further illustrate the potential complications and provide additional information, the following table highlights key points:
| Complications | Additional Information |
|---|---|
| Vision Loss | Corneal ulcers can cause permanent damage and lead to vision loss. |
| Cornea Scarring | Scarring on the cornea is a possible complication of corneal ulcers. |
| Contact Lens Wear | Wearing contact lenses, especially overnight, increases the risk of corneal ulcers. |
| Hygiene Practices | Proper hygiene practices, such as washing hands and cleaning contact lenses, can help prevent corneal ulcers. |
It is crucial to seek prompt medical attention if symptoms of a corneal ulcer develop or worsen, or if severe eye pain occurs. Remember to consult with an eye care provider for guidance, especially regarding contact lens usage and hygiene practices. By understanding the potential complications and taking necessary precautions, you can minimize the risk of corneal ulcers and maintain good eye health.
Definition and Alternative Names
To further understand corneal ulcers, it is important to define the condition and explore any alternative names it may have. A corneal ulcer is an open sore in the outer layer of the cornea, the clear tissue at the front of the eye. It is often caused by infection, with bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites being the common culprits. Alternative names for corneal ulcer include bacterial keratitis, fungal keratitis, acanthamoeba keratitis, and herpes simplex keratitis.
- Corneal ulcer: This term may evoke feelings of concern and urgency, as it signifies an open sore on the cornea, which can cause significant damage and even blindness if not treated promptly.
- Bacterial keratitis: The mention of bacteria as the cause of the ulcer may elicit a sense of vulnerability, as bacterial infections can be serious and require immediate attention.
- Herpes simplex keratitis: The inclusion of herpes simplex virus as a cause may create a sense of alarm, as this viral infection can lead to severe complications and require specialized treatment.
Understanding the different names for corneal ulcers helps to convey the seriousness of the condition and emphasizes the need for early diagnosis, prompt treatment, and preventive measures. By recognizing the various causes and risk factors, individuals can take steps to protect their eyes and seek appropriate medical care when necessary.
Causes
Corneal ulcers are most commonly caused by infections, including bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic. Bacterial infections, such as staphylococcus or pseudomonas, are a common cause of corneal ulcers. Viral infections, like herpes simplex or varicella, can also lead to the development of corneal ulcers. Fungal infections, although rare, can occur and may be caused by organisms such as Fusarium or Candida. Parasitic infections with Acanthamoeba can also cause corneal ulcers.
Wearing contact lenses, especially extended-wear soft contacts, increases the risk of corneal ulcers. Bacteria or particles trapped under the lens can lead to infection. It is essential to follow proper contact lens hygiene and care to reduce the risk of corneal ulcers.
Corneal dystrophies, which are genetic conditions that affect the cornea, can also increase the risk of developing ulcers. These conditions weaken the cornea and make it more susceptible to infections.
Untreated conjunctivitis, commonly known as pinkeye, can progress to a corneal infection and the development of ulcers if left untreated. It is crucial to seek prompt medical attention if you have symptoms of conjunctivitis to prevent complications.
Additionally, there is a correlation between herpes zoster, also known as shingles, and corneal ulcer development. Shingles can affect the cornea in some cases, leading to the formation of ulcers.
Understanding the various causes of corneal ulcers can help individuals take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatment to avoid potential complications and vision loss.
Corneal Injury and Diagnosis
Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial if you experience a corneal injury or suspect the presence of a corneal ulcer, as proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing further damage and preserving vision. Corneal injuries can lead to serious visual impairment, so it is important to understand the diagnostic techniques and management options available.
Here are three important points to consider:
- Diagnostic Techniques: To diagnose a corneal ulcer, your eye care provider will use a dye and a slit lamp microscope to examine the cornea. They may also take a sample from the ulcer for lab analysis. These diagnostic techniques help determine the cause of the ulcer and guide appropriate treatment.
- Corneal Ulcer Complications: If left untreated, corneal ulcers can cause long-term damage to the cornea and affect vision. Complications may include scarring on the cornea and severe vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent these complications.
- Corneal Ulcer Prognosis: The outcome of a corneal ulcer depends on its cause and location. Many people recover completely with only minor vision changes, but in severe cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary. Regular follow-up with your doctor is important to monitor the healing process and ensure proper management.
Preventing corneal ulcers involves practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands thoroughly before touching the eyes, cleaning and disinfecting contact lenses properly, and avoiding wearing contact lenses overnight. Proper techniques for inserting, cleaning, and storing contact lenses should be learned to reduce the risk of corneal ulcers.
Treatment Options
When treating a corneal ulcer, your eye care provider will explore various treatment options based on the cause and severity of the ulcer. The treatment options for corneal ulcers include the use of topical antibiotics, oral antibiotics, antiviral medications, antifungal medications, and in severe cases, a corneal transplant.
Topical antibiotics are commonly prescribed to treat bacterial corneal ulcers. These medications are applied directly to the eye and help to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Oral antibiotics may also be used, especially in cases where the infection has spread or is more severe.
In the case of viral corneal ulcers, antiviral medications are often prescribed. These medications help to control the viral infection and prevent further damage to the cornea. Antifungal medications are used to treat fungal corneal ulcers, which are less common but can be serious if left untreated.
In some cases, a corneal transplant may be necessary. This procedure involves replacing the damaged cornea with a healthy cornea from a donor. Corneal transplants are typically reserved for cases where other treatment options have been unsuccessful or if the corneal ulcer has caused significant vision loss.
It is important to follow your eye care provider’s recommendations and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the corneal ulcer heals properly and to prevent complications.